A study published in the journal Gut in 2007 (1) shows that an inflammatory substance, interleukin (IL) 15, is produced by the intestine when it’s subjected to different substances derived from gluten: 19-mer and 33-mer gliadin peptides.
It is known that in celiac disease, this innate response mediated by interleukin 15, damages the cells of the intestine, decreasing the absorption of nutrients and the capabilities of digestion of other food as well. IL 15 also causes the leaky gut syndrome, this is, an increase of the gut permeability that leads to allergies and intolerances to other food.
But in this study, even if IL15 was in every case produced by gluten, the biopsies of the intestine showed any damage in non-celiac people. The explanation given by the researchers was that there might be “a higher IL15‐sensitive response under the same stimulus, which might be mediated by a higher density of IL15 receptors in patients with celiac disease”.
Concerning the leaky gut syndrome, this was not analysed in non-celiac people. But Dr. Mouton (2) explains that gluten activates a substance called zonuline in the intestine, which leads to leaky gut in every case.
Moreover, the difference in celiac people is that gluten also triggers an adaptive immune system response, with the production of anti-transglutaminase, anti-endomysial and anti-gliadin antibodies, which can aggravate the damage to the gut even more.
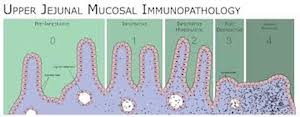
However, they conclude that “The data obtained in this pilot study support the hypothesis that gluten elicits its harmful effect, throughout an IL15 innate immune response, on all the individuals.”
The exact effect of this inflammatory substance, a part from the injury on the gut lining, is not yet detailed, but as every inflammatory substance, it surely must have a deleterious effect on everybody’s health. This must be true, because other studies link gluten to hundreds of different diseases, as it is exposed, for example, in this presentation by Dr. Peter Osborne “Gluten Sensitiviy, a Laymen’s Primer” and the book “The Dark Side of Wheat “ by Sayer Ji.
Quoting Sayer Ji in his article in GreenMedInfo.com “rather than look up the adverse gut responses associated with wheat, and particularly, wheat gliadin, as being a rare genetically-based aberration, we may want to reconsider the common, culturally reinforced view that wheat is an intrinsically healthy food that only an 'abnormal' subset of the human population has an 'unhealthy' response to. To the contrary, perhaps the immunoreactive effects that wheat gliadin induces indicates that we have a human species-specific intolerance to this 'food,' and that rather than look at these adverse effects as being 'unhealthy reactions to a healthy food,' perhaps we should look at them as 'healthy reactions to an intrinsically unhealthy (or metabolically incompatible) food.’ “
Instead of considering celiac people as sick people, I consider that they have a stronger immune system, and their body still is ringing the alarm against unhealthy food.
I think that when we are babies, our body refuses wheat products in different ways, in more or less strong reactions. This is one of the reasons for babies crying so much, having colic, reflux, eczema and other diseases (in order to know more about this topic, you can read this article). However, parents are not aware of the fact that the cause is wheat and other unsuitable food given to babies who are breastfed depending on their mother’s food, or included in infant formula, or in the first baby food. So the immune system becomes exhausted and turns off these alarms, the antibodies, without hope. So as we grow up, due to the innate inflammatory response, these first acute symptoms of food inadequacy become chronic diseases, as well as more and more life threatening diseases. As explained in this other article, opposed to what is commonly accepted, Natural Hygiene states that children have a more vigorous immune system than adults, and this is why they develop more acute diseases, while as we get older, we suffer more chronic diseases, because the body is unable to refuse and eliminate all the damaging substances. This is why doctors say that allergies disappear when children grow up, but they don’t mention that this happens at the expense of the appearance of other chronic diseases.
Concerning tests for gluten intolerance, following is some insight:
Other arguments why I recommend avoiding gluten are to be found in this other article
-----------------------------
(1) Gut. Jun 2007; 56(6): 889–890. “Is gliadin really safe for non‐coeliac individuals? Production of interleukin 15 in biopsy culture from non‐coeliac individuals challenged with gliadin peptides”
(2) "Écosystème intestinal et santé optimale", Dr. Georges Mouton
It is known that in celiac disease, this innate response mediated by interleukin 15, damages the cells of the intestine, decreasing the absorption of nutrients and the capabilities of digestion of other food as well. IL 15 also causes the leaky gut syndrome, this is, an increase of the gut permeability that leads to allergies and intolerances to other food.
But in this study, even if IL15 was in every case produced by gluten, the biopsies of the intestine showed any damage in non-celiac people. The explanation given by the researchers was that there might be “a higher IL15‐sensitive response under the same stimulus, which might be mediated by a higher density of IL15 receptors in patients with celiac disease”.
Concerning the leaky gut syndrome, this was not analysed in non-celiac people. But Dr. Mouton (2) explains that gluten activates a substance called zonuline in the intestine, which leads to leaky gut in every case.
Moreover, the difference in celiac people is that gluten also triggers an adaptive immune system response, with the production of anti-transglutaminase, anti-endomysial and anti-gliadin antibodies, which can aggravate the damage to the gut even more.

However, they conclude that “The data obtained in this pilot study support the hypothesis that gluten elicits its harmful effect, throughout an IL15 innate immune response, on all the individuals.”
The exact effect of this inflammatory substance, a part from the injury on the gut lining, is not yet detailed, but as every inflammatory substance, it surely must have a deleterious effect on everybody’s health. This must be true, because other studies link gluten to hundreds of different diseases, as it is exposed, for example, in this presentation by Dr. Peter Osborne “Gluten Sensitiviy, a Laymen’s Primer” and the book “The Dark Side of Wheat “ by Sayer Ji.
Quoting Sayer Ji in his article in GreenMedInfo.com “rather than look up the adverse gut responses associated with wheat, and particularly, wheat gliadin, as being a rare genetically-based aberration, we may want to reconsider the common, culturally reinforced view that wheat is an intrinsically healthy food that only an 'abnormal' subset of the human population has an 'unhealthy' response to. To the contrary, perhaps the immunoreactive effects that wheat gliadin induces indicates that we have a human species-specific intolerance to this 'food,' and that rather than look at these adverse effects as being 'unhealthy reactions to a healthy food,' perhaps we should look at them as 'healthy reactions to an intrinsically unhealthy (or metabolically incompatible) food.’ “
Instead of considering celiac people as sick people, I consider that they have a stronger immune system, and their body still is ringing the alarm against unhealthy food.
I think that when we are babies, our body refuses wheat products in different ways, in more or less strong reactions. This is one of the reasons for babies crying so much, having colic, reflux, eczema and other diseases (in order to know more about this topic, you can read this article). However, parents are not aware of the fact that the cause is wheat and other unsuitable food given to babies who are breastfed depending on their mother’s food, or included in infant formula, or in the first baby food. So the immune system becomes exhausted and turns off these alarms, the antibodies, without hope. So as we grow up, due to the innate inflammatory response, these first acute symptoms of food inadequacy become chronic diseases, as well as more and more life threatening diseases. As explained in this other article, opposed to what is commonly accepted, Natural Hygiene states that children have a more vigorous immune system than adults, and this is why they develop more acute diseases, while as we get older, we suffer more chronic diseases, because the body is unable to refuse and eliminate all the damaging substances. This is why doctors say that allergies disappear when children grow up, but they don’t mention that this happens at the expense of the appearance of other chronic diseases.
Concerning tests for gluten intolerance, following is some insight:
- Celiac disease: Blood IgA antibodies anti-transglutaminase and anti-endomysium; and sometimes IgA and IgG antibodies to deamidiated gliadin peptide; followed by an intestinal biopsy if antibodies test is positif. These tests use to be ordered by medical doctors when there's a suspicious of celiac disease.
- Gluten intolerance:
- Blood antibodies IgG to gluten. Some commercial tests are Imupro and Bloodspot IgG4 (non-invasive test).
- Stool antibodies IgA to gluten.
Other arguments why I recommend avoiding gluten are to be found in this other article
-----------------------------
(1) Gut. Jun 2007; 56(6): 889–890. “Is gliadin really safe for non‐coeliac individuals? Production of interleukin 15 in biopsy culture from non‐coeliac individuals challenged with gliadin peptides”
(2) "Écosystème intestinal et santé optimale", Dr. Georges Mouton
 A research study shows that the innate immune system reacts against gluten in both celiac and non-celiac people producing interleukins, a kind of inflammatory substances. That means that we all are indeed sensitive to gluten.
A research study shows that the innate immune system reacts against gluten in both celiac and non-celiac people producing interleukins, a kind of inflammatory substances. That means that we all are indeed sensitive to gluten.







 Gemma Calzada es doctora en Salud Holística y terapeuta GAPS. Su objetivo es mejorar la salud con la nutrición y el estilo de vida, y ayudar a las personas que sufren intolerancias alimentarias a vivir felices.
Gemma Calzada es doctora en Salud Holística y terapeuta GAPS. Su objetivo es mejorar la salud con la nutrición y el estilo de vida, y ayudar a las personas que sufren intolerancias alimentarias a vivir felices. 
